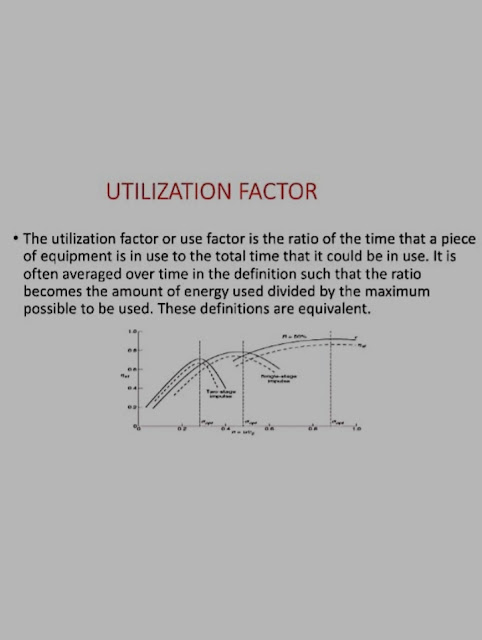
The utilization factor and space height ratio are two important factors in the design of buildings, particularly in the design of office buildings. The utilization factor is a measure of how efficiently a building space is used, while the space height ratio is a measure of how much space is available in a building relative to its height. In this article, we will discuss the utilization factor and space height ratio and their importance in building design.
The utilization factor and space height ratio are two important factors in the design of buildings, particularly in the design of office buildings. The utilization factor is a measure of how efficiently a building space is used, while the space height ratio is a measure of how much space is available in a building relative to its height. In this article, we will discuss the utilization factor and space height ratio and their importance in building design.The utilization factor (UF) is a measure of the efficiency with which a building space is used. It is the ratio of the usable floor area of a building to its gross floor area. The usable floor area is the total floor area of a building that can be occupied by people or equipment, while the gross floor area is the total floor area of a building, including walls and other non-usable areas.
The utilization factor is typically expressed as a percentage. For example, if a building has a usable floor area of 10,000 square feet and a gross floor area of 15,000 square feet, its utilization factor is 67% (10,000/15,000).
Space Height Ratio:
The space height ratio (SHR) is a measure of the amount of space that is available in a building relative to its height. It is the ratio of the total usable floor area of a building to its total height. The total height of a building is the height from the floor to the ceiling of the highest occupied floor.
The space height ratio is important in the design of office buildings because it determines the amount of natural light that can enter a space. A higher space height ratio means that there is more natural light available in a space, while a lower space height ratio means that there is less natural light available in a space. The optimal space height ratio depends on the type of building and the needs of the occupants.The space height ratio is typically expressed as a ratio. For example, if a building has a total usable floor area of 10,000 square feet and a total height of 100 feet, its space height ratio is 100:1 (10,000/100).
Relationship Between Utilization Factor and Space Height Ratio:
The utilization factor and space height ratio are related to each other because they both affect the amount of space that is available in a building. A higher utilization factor means that there is less space available per occupant, which can be compensated by a higher space height ratio to provide more natural light to the occupants.
On the other hand, a lower utilization factor means that there is more space available per occupant, which can be compensated by a lower space height ratio to reduce the amount of natural light that enters a space. The optimal utilization factor and space height ratio depend on the needs of the occupants and the type of building.
Conclusion: